Assignment 9.1: Creating a Graph (4 points)
Your task is to create a class Graph in python which stores a weighted directed or undirected graph structure. The initializer method takes a \(V \times V\) weighted adjacency matrix as an input value (\(V\) sized list of \(V\) sized lists).
The class must have following methods:
- df_print(start: int): prints out the graph in depth-first order from the start vertex (vertex numbers separated by space).
- bf_print(start: int): prints out the graph in breadth-first order from the start vertex.
- weight(vertex1: int, vertex2: int): returns the weight from vertex1 to vertex2, returns -1 if there is no edge between the vertices.
where start vertex is labeled between \(0\ ...\ V-1\).
Feel free to store the graph structure to your class as you wish as long as the given functions above work as intended. You can use the adjacency matrix
or create a adjacency list to keep track of neighbors of each vertex (or even both).
Note: This graph class will be used in following assignments related to graphs so it is recommended to complete this assignment before moving to others.
A code template with an example program for the directed graph below:
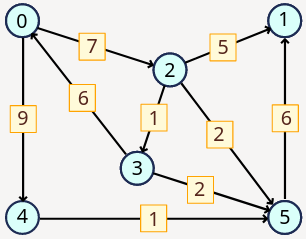
class Graph:
# TODO
if __name__ == "__main__":
matrix = [
# 0 1 2 3 4 5
[0, 0, 7, 0, 9, 0], # 0
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], # 1
[0, 5, 0, 1, 0, 2], # 2
[6, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2], # 3
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1], # 4
[0, 6, 0, 0, 0, 0] # 5
]
graph = Graph(matrix)
graph.df_print(0) # 0 2 1 3 5 4
graph.bf_print(0) # 0 2 4 1 3 5
print(graph.weight(0, 2)) # 7
print(graph.weight(3, 4)) # -1
Submit your solution in CodeGrade as graph.py.
Assignment 9.2: Dijkstra's Algoritmh (4 points)
With Dijkstra's algorithm we not only get the shortest paths from the start vertex to other vertices but we can build a new
graph with only the arcs that constructs those paths.
Create a function dijkstragraph(graph: Graph, start: int) that takes a Graph object and the start vertex as an input value. The function
returns a new Graph object that has only the arcs that constructs the shortest paths computed by Dijkstra's algorithm. The new graph will be directed despite
whether the original graph was directed or undirected.
For example the on the left we have the original directed graph and on the right we have a graph that the function produces, starting from vertex \(0\).
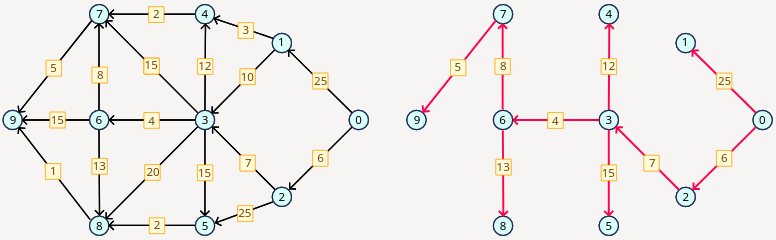
A code template with an example program for the graph:
from graph import Graph
def dijkstragraph(graph, start):
# TODO
if __name__ == "__main__":
matrix = [
[0, 25, 6, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 10, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 7, 0, 25, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 12, 15, 4, 15, 20, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 8, 13, 15],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 5],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
]
graph = Graph(matrix)
new_graph = dijkstragraph(graph, 0)
new_graph.df_print(0) # 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 8
new_graph.bf_print(0) # 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
print(new_graph.weight(3, 6)) # 4
print(new_graph.weight(5, 8)) # -1
Submit your solution in CodeGrade as dijkstra.py including your graph class in graph.py (Assignment 9.1).
Hint: try to do the Dijkstra's algorithm and new graph construction separately. What other information can we get while running Dijkstra's algorithm?


